Content
Myoma is a benign neoplasm of a hormone-dependent nature, localized in the muscular layer of the uterus. Pathology is typical for women from 30 to 45 years old, but can also develop at a younger age. If you start when the formation is small, you can avoid surgery, as well as more serious indications in the form of removal of the organ.
The feasibility of surgical treatment
Uterine fibroids form and develop in a muscular layer called the myometrium. Upon reaching a significant size, the formation can migrate and be diagnosed:
- in the body of a muscular organ;
- in the neck part.
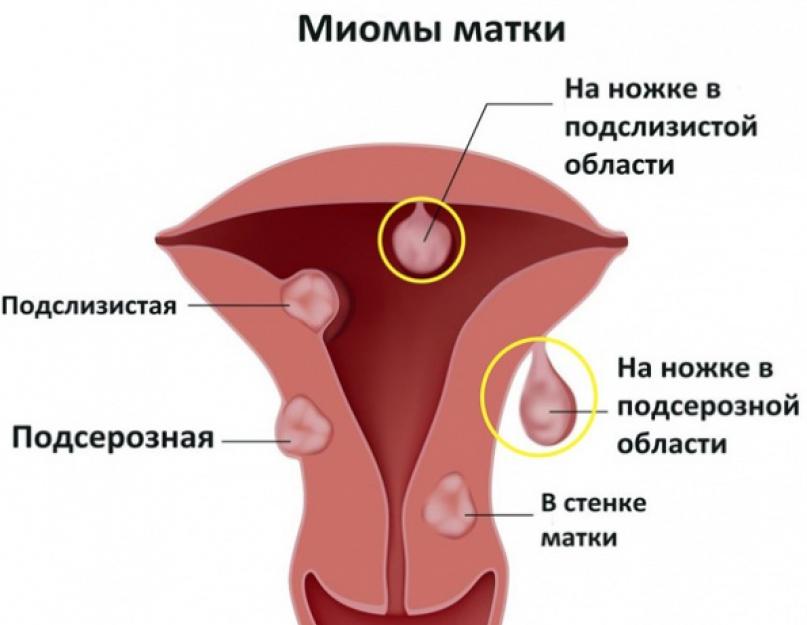
Specialists distinguish the following options for fibroids regarding its localization in the uterus:
- subserous, located under the serous membrane;
- submucosal or submucosal, is located under the mucous membrane;
- intramural or interstitial, grows in the thickness of the myometrium;
- intraligamentary, progresses between the leaves of the broad ligament;
- retroperitoneal, grows from the cervical part.
Uterine fibroids usually have the form of nodes, which are characterized by a different number and size:
- multiple and single tumor;
- neoplasm of small, medium or large sizes.
Large nodules are often an indication for surgery or removal of the uterus. Myomatous nodes are attached to the tissue of the uterine wall through a wide base or thin stem. The growth rate of neoplasms depends on the structure.
- Simple fibroids grow slowly and reach significant volumes within five years.
- Proliferating tumor characterized by rapid progression.
- Presarcoma contains altered cells, characterized by the presence of several large nuclei.
Histological composition may differ. If the formation contains predominantly smooth muscle cells in the structure, leiomyoma is diagnosed. Fibrous tissue in the composition of the tumor characterizes fibromyoma.
Myoma has a hormone-dependent etiology and pathogenesis. Congenital disorders occurring in the muscular tissue of the uterus under the influence of internal and external adverse factors are also considered as the cause of the formation of a neoplasm.

Before treating the disease, it is necessary, if possible, to eliminate the factors that provoke the progression of the nodes. Otherwise, the treatment may be useless, which will lead to tumor growth and an indication for its surgical removal.
The severity of the clinical picture is essential when choosing treatment tactics. Often, the disease proceeds latently, which contributes to its rapid progression and detection at an advanced stage. This explains why doctors often have to remove nodes surgically.
Features of the clinical picture are often an indication for surgery.
There are certain indications for both the removal of fibroids and the body of the uterus.
Doctors distinguish the following indications for the removal of fibroids:
- leiomyoma size at least 12 weeks;
- combination of fibroids with endometriosis or cancer;
- torsion of the legs of fibromyoma, its necrosis;
- violations of the functioning of internal organs;
- severe pain;
- oncological alertness;
- reproductive disorders;
- lack of effect from the use of drugs that stop acyclic.
The following sizes of nodes are called, which correspond to the weeks of pregnancy:
- a small fibroid corresponds to five weeks of pregnancy and two centimeters;
- secondary education, equivalent to a pregnancy for a period of eleven weeks and having a size of up to six centimeters;
- a large tumor looks like a 15-week pregnancy with nodes that have a volume of more than six centimeters;
- with a giant neoplasm an increase in the uterine cavity reaches 16 weeks or more.
A large or giant fibroid is an indication for removal. Sometimes doctors have to remove small fibromyomas, in particular, with torsion of the leg, necrosis of the formation, infertility. A few decades ago, gynecologists believed that with fibroids, the uterus should be removed.
In recent years, indications for hysterectomy have been reduced to a minimum. In modern gynecology, large fibroids and the onset of menopause are no longer indications for removal of fibroids.
It is necessary to remove the uterus with myoma in the following cases:
- suspicion of oncology;
- concomitant prolapse of the uterine body and cervix;
- active progression of endometriosis.
When a woman's uterus is removed, she not only loses her reproductive function. Removal of the uterus will necessarily entail serious consequences for health. In this connection, organ-preserving operations are carried out in modern gynecology. Removal of the uterus is necessary only for certain indications.
Operation methods
If indicated, uterine fibroids should be removed. Before removing the neoplasm, the doctor must conduct an examination to determine the exact location and type of leiomyoma.
When indications for surgical treatment of fibromyomas are carried out using:
- organ-preserving treatment;
- radical operations.
For small fibroids, the indication is treatment with sparing tactics, for example, uterine artery embolization, myomectomy, FUS ablation. During such operations, the myomatous node is removed, and the reproductive function is preserved.
Embolization of the uterine arteries consists in removing the node by blocking the vessels that feed it. Such removal of fibroids refers to an effective technique with a relatively low percentage of relapses.

Organ-preserving removal is carried out by several techniques.
- Laparoscopic and laparotomic myomectomy. Indications for removal are single and multiple tumors of the interstitial or subserous variety. Laparotomy removal is used quite rarely due to trauma and the risk of surgical complications. Among the indications for the isolation of large leiomyomas, uterine deformities.
- . Removal must be carried out using a hysteroscope with a submucosal location of the tumor. During this manipulation, gynecologists have to both diagnose and remove leiomyomas. The operation is also performed at the birth of the submucosal node. Removal must be performed in the first days of the cycle during a planned operation. You can remove fibroids in a hospital and outpatient setting.

When using surgical methods of treatment, it is necessary to take into account that the removal of uterine fibroids is often accompanied by a risk of complications and relapses.
In gynecological practice, sometimes doctors have to remove uterine fibroids using a radical method. Radical surgery requires removal of the uterus. Radical surgeries include:
- hysterectomy;
- extirpation.
After the surgical treatment The patient is undergoing medical examination. As a rule, a woman also has to take hormonal drugs to prevent relapse.
Hysterectomy
A uterus with fibroids can be removed with an operation called a hysterectomy. This intervention ranks second in frequency in women. Experts note that this is one of the most common ways to remove fibroids.
Absolute indications, in which it is necessary to remove the uterus in case of myoma, are the processes of its prolapse or prolapse, as well as the suspicion of cancer. Hysterectomy is often necessary for women to remove a uterus with advanced tumor after menopause.
With fibroids, the removal of the uterus can be carried out in different ways. There are several types of hysterectomy, with which you can remove the body:
- subtotal, consisting in the removal of the uterus while preserving its cervical part;
- total, meaning the removal of both the uterus and its cervix;
- hysterosalpingo-oophorectomy, implying the removal of the uterine body, ovaries, and tubes.
Before removing the affected organ, the doctor must warn about the complications that may arise during and after the hysterectomy. Complications after a hysterectomy include:
- allergic reactions to anesthesia, leading to death;
- damage to organs located in the pelvis, as well as nerve bundles;
- postoperative bleeding;
- intestinal obstruction;
- development of the adhesive process;
- peritonitis.
After removal, the patient needs to carefully monitor her well-being. In the absence of complications, recovery after a hysterectomy will take about two months.

Hysterectomy has a number of distant ones that adversely affect a woman's life. The long-term consequences after removal by the hysterectomy method include:
- posthysterectomy syndrome;
- exacerbation of diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- the risk of developing a tumor in the mammary glands;
- the development of manifestations of menopause, for example, depression and sweating, hot flashes, osteoporosis;
- problems in intimate life due to the occurrence of vaginal dryness, decreased libido;
- prolapse of the vaginal walls;
- urinary incontinence;
- bacterial vaginosis;
- hypertension;
- obesity.
The patient after the removal of the uterus, which implies a hysterectomy, must take hormonal drugs. After a hysterectomy, a woman loses her reproductive function, which is especially important for women of childbearing age.
Many modern gynecologists say that it is not always worth removing an organ through a hysterectomy. In some cases, an organ-preserving intervention is required. Before deciding on a hysterectomy and removing an organ, one must think about the consequences that may appear in the long term.
29.04.2017
Uterine fibroids is a pathology that consists of blood vessels and connective tissue. It grows from the muscular layer of the organ, and may look like a single or multiple node.
When diagnosing a tumor, the first thing the patient asks the doctor is whether it is necessary to remove the fibroid.
Causes of the appearance of pathology
Doctors identify several main causes of the appearance of such a tumor, these are:
- Hormonal disbalance.
- Low immunity.
- genetic predisposition.
Tumor types
There are three types of fibroids:
- Submucosal - means that the pathology grows inside the uterus.
- Subserous - try to get out of the organ.
- Interconnective.
On average, pathologies are diagnosed with a size of about fifty millimeters, although it can grow up to one hundred millimeters. But large tumors are a rarity.
Symptoms of the disease
It should be noted that in the early stages, the disease does not show any symptoms, so it is very difficult to diagnose it. Although this can happen if a woman undergoes a preventive examination by a gynecologist.
But if the disease is running, the tumor has already reached a sufficiently large size, then certain symptoms appear, namely:
- Profuse and prolonged menstruation.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Infertility (spontaneous miscarriage or premature birth in which the child does not survive).
If fibroids do not pose any danger to a woman's health, doctors recommend treatment with medications. However, it rarely gives a positive result and ultimately, the tumor has to be removed surgically.
Is it possible to cancel the operation
Speaking specifically about the removal of the uterus, then such an operation is recommended to be carried out when a woman has crossed the line of forty years. At this age, women already have children, they no longer plan to give birth, so they no longer “need” the uterus.
If a woman agreed to such an operation, then before performing it, the doctor should observe the development of the pathology for some time. Find out how fast it grows and only after that make a decision about removal.
For the operation to take place, certain indications are necessary:
- The patient is over forty years old.
- The size of the pathology is more than twelve weeks of pregnancy.
- The development of fibroids for more than four weeks a year.
- The degeneration of a neoplasm into a cancerous tumor. The age of the patient will not be taken into account, as well as the presence of children. Because the focus will be on her life.
 In medicine, there are cases when fibroids resolve themselves, during the period when a woman reaches menopause. At this time, the body stops producing estrogen, which feeds the pathology, and over time, the tumor disappears. It doesn't happen in one month, it can take years. If everything goes well, then the operation can not be carried out.
In medicine, there are cases when fibroids resolve themselves, during the period when a woman reaches menopause. At this time, the body stops producing estrogen, which feeds the pathology, and over time, the tumor disappears. It doesn't happen in one month, it can take years. If everything goes well, then the operation can not be carried out.
If the patient is diagnosed with many fibroids, then she is sent for examination. Having studied its results, the doctor will be able to clearly understand the whole picture of the pathology, and only after that will make a decision about the removal.
If the disease is found in a woman who is under forty years of age, then the decision to remove will be made in order to save the organ and remove only the tumor.
The question of whether it is necessary to remove uterine fibroids can be answered as follows: if the woman's age has crossed the forty-year limit, then the entire organ must be removed. Thus, doctors will save a woman from possible relapses and cancerous pathologies.
The main indications for surgery
So, there are certain indications that indicate the need to remove the pathology, regardless of the age of the woman:
- The size of the neoplasm is more than twelve weeks.
- The rapid growth of pathology.
- With the appearance of heavy bleeding, not only during menstruation, but also between it.
- development of anemia.
- The appearance of fainting.
- With pain that occurs due to the fact that the neoplasm begins to compress neighboring organs or nerve endings.
- Negative changes in the structure of pathology.
- With a formation growing on a thin, long base, by which it is connected to the uterus. In this case, the leg may twist and bleeding will occur.
- The location of the tumor in the cervix.
- Infertility due to this pathology.
Any disturbances in the functioning of the organs located near the neoplasm can affect the removal:
- Violation of the emptying of the bladder. Because of this, urine can accumulate in it, and this leads to inflammation, sand and stones.
- The ingress of urine into the ureter, which causes inflammation and pyelonephritis.
- Due to the clamping of the rectum, defecation is not going well. The consequence of this is constant constipation, and then poisoning of the body.
- Squeezing of the nerve endings near the rectum, because of this there is pain in the heart, lower back and legs.
Surgical removal of fibroids
Before determining which method will be used to remove the pathology, it is necessary to consider the following factors:
- The age of the woman.
If the patient is not yet forty years old, then only the neoplasm is removed, without touching the uterus. After forty, the removal of an organ is possible because it has already fulfilled its main role in a woman's life.
- Tumor size twelve weeks.
- The location of the neoplasm, if it is found on the back wall of the uterus.
If the removal is directed only at the tumor itself, then the pathology may occur again, after some time.
With a small tumor, it is necessary to monitor its further development. If it does not increase and does not cause discomfort to the patient, then surgery is not required. A woman needs to regularly undergo preventive examinations in order to see the changes in time and make the right decision.
Varieties of operations
There are several types of surgical treatment:
- Laparotomy. To excise the tumor in this way, you will have to make an incision in the patient's abdomen. The main indications of this method are a large or multiple neoplasm that deforms the organ itself. A good prevention would be a woman's pregnancy two years after the operation.
- Laparoscopy. To do this, you do not need to cut the stomach, only its piercing is required, which subsequently does not leave scars. The most appropriate indication would be a small tumor size, about nine weeks. If this method is applied to a large pathology, then bleeding from the uterus may occur.
- Hysteroscopy. No incisions or punctures are required during this process. The operation is performed through the vagina. Indications are small neoplasms, a pathology on the basis, a pathology that degenerates into a cancerous tumor.
- Hysterectomy. Excision of not only neoplasms, but also of the uterus, which can be carried out through an incision in the abdomen or vagina. This method is used if the tumor is critical and can threaten the woman's life. Such removal is carried out mainly by women after forty years of age, but if the situation is critical, then it can be prescribed to patients who have not reached this age.
- Embolization. In this case, the blood vessels are clogged and the neoplasm, due to lack of nutrition, slowly dies off.
Condition of a woman after removal of the uterus
 After the removal of the organ, the following consequences may occur:
After the removal of the organ, the following consequences may occur:
- Depressive states of a woman.
- Mental disorders.
- Pain syndrome in the pelvis.
- Violations in the work of the genitourinary system.
- Lack of orgasm.
- Loss of interest in sexual activity.
- Early menopause (if ovaries remain).
The main thing is that doctors remember that there are no “extra” organs in the body, so you should think about it before completely removing the uterus.
Article last updated 07.12.2019
Often, after a preventive examination by a gynecologist, many women are told a terrible diagnosis - uterine fibroids. Progressing in the body, this disease leads to severe complications, therefore, at an advanced stage, the only true method of treatment is the removal of the uterus with myoma.
But do not despair. Now there are various sparing methods of treatment while maintaining reproductive function. In each case, the gynecologist must assess the size and location of the tumor and tell the patient about acceptable treatment options.
At an early stage, a benign tumor (myoma) responds well to conservative drug treatment. But if the tumor does not respond well to drug therapy and the tumor grows, doctors prescribe surgery.
In severe cases, emergency drastic measures may be required when the fibroid is removed along with the uterus. Surgical intervention allows you to quickly save a woman from the painful symptoms of pathology, but at the same time, the ability to become pregnant is completely lost.
Reviews of doctors about the removal of the uterus with myoma confirm that after the operation the quality of life of women improves much. Hysterectomy saves the patient from persistent uterine bleeding, which sometimes has to be stopped by curettage (cleaning) of the uterine cavity.
Large blood loss leads to iron deficiency anemia, which requires serious therapy. Sometimes you even have to do a blood transfusion.
Against the background of severe pain and depression, psycho-emotional problems appear. In addition, if there is a suspicion of the development of oncology, this is a direct indication of the removal of the uterus with myoma.
Before removing the uterus with fibroids, the doctor must conduct a thorough examination. With a wide choice of different methods of surgical intervention, based on medical statistics, hysterectomy is most often prescribed.
More than a million such surgeries are performed in Russia every year. Young women tend to try to save the uterus.
Important! The absolute indication that determines the urgency of the operation is the transformation of a benign neoplasm into a cancerous tumor.
Gynecologists come to the conclusion that it is necessary to remove the uterus if:
- Pronounced symptoms of pathology lead to health problems.
- Myoma has reached a significant size, exceeding 12-14 weeks of pregnancy.
- The patient suffers from severe pain or constant bleeding.
- Pain in the small pelvis of a chronic nature.
- The presence of numerous myomatous nodes.
- An increase in tumor volume led to prolapse of the uterus.
- There is a risk of tumor necrosis as a result of twisting of its legs.
- The fibroid is very large and presses on nearby organs.
- The last stage of endometriosis.
- Recurrent polyps.
- The patient is close to menopause.

The above indications make you seriously think about maintaining health. That is why the attending physician must assess all the risks and offer the patient the most optimal method of treatment.
Operation methods
If the attending physician after the diagnosis proposes to remove the fibroids along with the uterus, it is necessary to determine the method of surgical intervention.
Supravaginal amputation of the uterus is often performed without removal of the appendages. Only the body and cervix are removed through the vaginal incision. Also acute is the question of the preservation of the ovaries. The ideal option is to preserve both the ovaries and the cervix.
Types of surgery
Laparoscopy- is a gentle operation. The surgeon makes three microscopic punctures in the abdominal wall. Next, a laparoscope is inserted into the hole - a surgical instrument in the form of a long needle - and the necessary manipulations are carried out. Surgery is performed under general anesthesia.

Laparotomy- dissection of the anterior wall of the peritoneum. After the operation, the incision leaves a small but noticeable scar. Over time, the seams will become less noticeable, but will not completely disappear. Laparotomy is performed under general anesthesia, the rehabilitation period is about two months. Now this type of operation in medicine is rarely practiced, since it is possible to use less traumatic methods.
Hysteroscopy- most commonly used. Myoma is removed with a hysteroscope, which is inserted through the cervical canal. At the same time, the abdominal wall remains intact, which eliminates damage and shortens the rehabilitation period. According to patients, this is the best method for treating fibroids.

Hysterectomy- complete amputation of the uterus, the most serious and complex operation. After this surgery, there are often severe complications. Every thousandth operation ends in death. It should be noted that hysterectomy with preservation of appendages practically does not cause hormonal changes in the body. The hormonal background normalizes over time, the patient's libido is completely preserved. The recovery period will take several months. Psycho-emotional recovery is also important.

Is abdominal surgery dangerous to remove the uterus?
Removal of uterine fibroids surgically is a forced measure that requires careful preparation and control over the operation. Regardless of the methods of extirpation, there is always a high probability of side effects and complications. The possible consequences after emergency removal of the uterus with fibroids greatly frighten many women.
The worst thing that can happen is the death of a patient. In 90% of cases, death occurs due to complications during the administration of anesthesia.
Sometimes there is mechanical damage to the vessels, nerves and organs surrounding the uterus. The human factor plays an important role in the successful completion of the operation. Even the most skilled surgeon is not immune from mistakes. Laparoscopic hysterectomy is complicated by large blood loss. It is very difficult to ligate the vessels and stop the bleeding with endoscopic instruments.
Extirpation of uterine fibroids- a rather complicated operation, during which blood, particles of talc from surgical gloves can enter the cavity. This leads to the formation of adhesions and can cause intestinal obstruction in the patient. The only way to correct the situation is through re-intervention.
Peritonitis, inflammation of the abdominal mucosa, abscesses - all these negative consequences arise due to non-compliance with the technique of extirpation and improper wound treatment after surgery.
It is important to understand that even in the absence of complications, the recovery of a woman's body after removal of uterine fibroids lasts at least two months.
What is the danger of removing the uterus for a woman in the future
The consequences of the removal of the uterus can manifest themselves for quite a long time.
Unfortunately, more than 70% of women develop post-hysterectomy syndrome after surgery.
Most often, this condition occurs against the background of a reduced level of estrogen in the patient's body. Most doctors agree that only if there are two ovaries, it is possible to delay the development of menopause during hysterectomy as much as possible (by 5-6 years). But at the same time, the younger the patient, the earlier she may experience estrogen deficiency.
A low level of the hormone estrogen is an impetus for the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system. So, for women under the age of 50 who have undergone an extirpation procedure, the risk of developing heart pathologies increases significantly.
According to statistics, removal of the uterus increases the likelihood of developing thyroid and kidney cancer. It is impossible to predict exactly what consequences await a woman after extirpation. Patients note the manifestation of such signs of menopause as: an unstable psycho-emotional state, insomnia, a feeling of heat. Already at the age of forty, a woman can feel all the “charms” of postmenopause.

Impaired metabolism, in particular calcium deficiency, is a common cause of osteoporosis. Estrogen deficiency causes dryness in the vagina and significantly reduces the quality of sexual life. A woman ceases to experience an orgasm, the number of sexual acts decreases significantly. The natural functioning of the urinary system is disrupted.
More than 20% of patients develop urinary incontinence. Failures in the work of the endocrine system of a woman lead to obesity (every third patient suffers).
Alas, not every woman understands what threatens the removal of the uterus, so many are so frivolous about their health. Further consequences of surgical removal of the uterus along with fibroids have been pursued for many years.
Alternative ways
Numerous complications during and after the operation prompted scientists to develop safer methods for treating fibroids. There are several commonly practiced alternative ways to deal with fibroids:
- FUS ablation is an experimental approach to removing fibroids. The principle of operation of this method: myoma formations are exposed to ultrasonic radiation.
- Myomectomy- surgical removal of fibroids. The surgeon removes the fibroids while sparing the uterus.
- UAE (uterine artery embolization)- an alternative treatment in which special balls - emboli - are introduced into the uterine cavity. They block the blood flow in myomatous formations, thereby causing the process of their necrosis, death.

Important! Complications after extirpation can be different, but the most tragic experience for women is the inability to become pregnant and give birth to a baby in the future.
Also, do not forget about the psycho-emotional side of the issue. Many women after the operation feel some inferiority, it is especially difficult to establish intimate contact with a partner in the same volume. Removal of the uterus, according to patients, is more difficult to tolerate at a young age.
Features of the postoperative period
How long the recovery period lasts depends on the chosen surgical treatment. Complicated abdominal surgery implies the longest recovery period. Definitely, a woman will have to reconsider the usual rhythm of life for some time, change her diet.

Only strict adherence to the rules of rehabilitation gives some guarantee of the absence of postoperative complications. If all the recommendations are followed unquestioningly, then in four months the patient will be able to return to her usual life.
To reduce the risk of side effects and speed up the recovery process, you need to undergo a series of rehabilitation measures:
- Kegel exercises. Removal of the uterus can cause a change in the location of the pelvic organs. The natural functioning of the bladder and intestines is disrupted. The patient suffers from constipation, urinary incontinence. The muscles of the pelvis are so weakened that the vagina can simply fall out. You can correct the situation with the help of Kegel exercises.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy helps to prevent the development of menopause in women. The list of mandatory drugs includes drugs with a high content of the hormone estrogen. They may be in the form of tablets, patches, ointments or gels.

- Diet and diet. With hormonal imbalances, there is always a high risk of gaining excess body weight. To avoid this, it is worth reviewing your diet, giving preference to healthy foods with a minimum content of fat and salt.
It is worth noting that in women who have undergone extirpation, menopause in most cases occurs much earlier. But with the help of hormone therapy, you can reduce the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms. It is also important to lead an active lifestyle and in no case give up sexual relations. If there are no postoperative complications, then after a month and a half you can have sex. Do not withdraw into yourself and do not reject the support of loved ones.

Removal of the uterus is not a sentence at all, as some women believe. Careful observance of all the doctor's recommendations ensures that the quality of life of the patient does not change, and perhaps it will become better and acquire a new meaning. Before the operation, a positive psycho-emotional attitude is extremely important, then it will be much faster to return to normal life.
Uterine fibroids is one of the most common gynecological pathologies, and you will not surprise anyone with such a diagnosis. According to statistics, the disease is detected in 35% of women over the age of 35 years. In modern gynecology, practitioners often have to deal with formations of small and medium sizes.
Large-sized fibroids are somewhat less common due to the developed diagnostic system and the timely passage of regular medical examinations by women. It is noted that huge nodes are detected mainly after 40 years in patients who have refused treatment for a long time.
The largest fibroid in the world, according to medical literature, weighed 63 kilograms, and so far this sad record has not been broken. This fact makes it clear: a uterine tumor can grow almost indefinitely, reaching gigantic proportions. There is no need to wait until the weight of the fibroids is equal to the weight of an adult. Timely therapy avoids such a development of events and prevents the rapid growth of the myomatous node.
What fibroid is considered large
On numerous forums on the Internet, you can find entries in the style of “I have been living with a large fibroid for many years, I don’t know what to do.” At the sight of such messages, women involuntarily ask themselves the question: which fibroids should be considered large and are there clear criteria for this condition (for example,)? Gynecologists adhere to the generally accepted classification, according to which a large fibroid is considered a node with a size of 6 cm (60 mm).

A large tumor is considered to be more than 6 centimeters in size (the photo shows a fibroid removed along with the uterus more than 15 cm in diameter).
The size of the uterus in this case corresponds to a 12-week pregnancy. But here are some important points to note:
- In the medical literature, one can find a mention that a large fibroid is a node with a diameter of 5-6 cm. In this situation, it is not entirely clear which category a tumor with a size of 5 or 5.5 cm belongs to - medium or large nodes? If we analyze the case histories of patients, we can see that fibroids of such borderline sizes are classified as both large and medium tumors. Practitioners in this situation are advised to look not only at the size of the formation, but also at the size of the uterus, and if it exceeds 12 weeks, classify the tumor as large;
A photo of a large fibromyoma can be seen below:

- With the leading value is the size of the dominant node - they are guided by it when drawing up a treatment protocol;
- Giant fibroids deserve special attention among large formations. Which tumor to consider as such is a debatable question. It is customary to refer to giant nodes from 10-12 cm in diameter. Such formations are poorly amenable to conservative therapy, and their removal within healthy tissues requires special skill of the surgeon. Often, with giant tumors of the uterus, the only method to solve the problem becomes.
A photo of a giant fibroid is presented below:

On a note
Uterine leiomyoma according to ICD-10 has code D25, regardless of the size of the node.
It is important to understand that theoretically a benign tumor can reach any size if its growth is not limited by anything.
Distinctive features of large myomatous nodes
It's important to know
If a woman is planning a pregnancy, treatment of a large fibroid should not be delayed.
Successful conception of a child does not mean that the pregnancy will pass without complications. With large fibroids, placental insufficiency and concomitant fetal growth retardation are often recorded. Pregnancy against the background of a large tumor can end prematurely, and rarely any of the women manage to bring the baby to at least 36-37 weeks.
Childbirth with myomatous nodes from 6 cm in size is quite often complicated by anomalies of labor activity and bleeding. According to the reviews of women who gave birth with a large fibroid, it becomes clear: the percentage of cesarean section in this case is very high.

With large fibroids, a woman can hardly give birth on her own. In this case, as a rule, a caesarean section is used.
- Fitness and sports. Intense exercise that increases blood flow to the pelvic organs is not recommended. It is forbidden to train the press and pelvic muscles;
- Yoga. You can do it, but asanas that affect the abdominal muscles are excluded;
- Visiting the sauna and bath. Although the effect of heat on the growth of the myomatous node has not been proven, gynecologists do not recommend getting involved in such procedures;
- Taking medication. Do not take drugs that can affect the growth of fibroids.
There are no special prohibitions regarding intimate hygiene. A woman can use panty liners, absorbent pads, and tampons (such as Tampax). The latter option is not very convenient, since it does not always allow you to fully assess the amount of bleeding during bleeding. There is no prohibition on sexual life, provided that the woman feels well.
The prognosis for large myomatous nodes depends on the timeliness of diagnosis. The sooner a tumor is detected and treatment is started, the easier it will be to stop its growth and prevent the development of complications.
Treatment methods for large fibroids
Case study: removal of a giant uterine fibroids
Diseases of the female reproductive system in some cases are detected quite by accident, for example, during the next scheduled examination, or in the diagnosis of concomitant diseases.
In this case, the disease does not yet have severe symptoms due to the initial stage of the course. Symptoms begin to appear as the disease progresses.
What is this tumor
Fibroids are benign growths localized in the body of the uterus or in organ, which can have both a single formation and represent a grid .
A benign tumor can be, it can grow rapidly or have a slow development.
The development of a nodular formation begins with the cells of the myometrium - the cells of the inner mucous layer of the uterus. In addition, fibroids can be of different types, have different symptoms and structure.
Myoma is of different types. It can be classified according to different features.
Depending on the cellular structure, the tumor is:
- simple. Has a cellular structure that is not able to divide;
- proliferating. 25% of tumor cells are able to divide, the rest of the cells have a cellular composition similar to simple myoma;
- presarcoma. Many nodular formations are concentrated in one tumor, 75% of the cells of which have mitotic activity.
By location, a benign neoplasm can be:
- (intramuscular). Such a fibroid is large and is located in the muscular layer of the body of the uterus;
- . This type of fibroids is located in the myometrium, on the border with the serous layer. A feature of the growth of such a formation is a strong growth in the abdominal cavity. A characteristic feature of the structure of such a tumor is a thin stalk on which the growth rests;
- (submucosal) . Such a tumor grows in the mucous layer of the uterus inside her body. When large, this tumor causes severe bleeding and pain.
A rare case when fibroids grow in the retroperitoneal region.
Depending on the cellular structure, fibroids are of two types:
- fibromyoma. Consists of connective tissue;
- leiomyoma. The cell structure of this species has a muscular-fibrous structure.
In accordance with the stage of development, there are three types of fibroids, each of which is characterized by the size of the node depending on the growth and time of development. The first stage has, the third is large, characterized by rapid growth.

Sizing principle
In order to indicate the size of a benign formation, experts take as a basis not only its diameter, but also the corresponding increase in the uterus.
With the growth of a benign tumor, an increase in the uterus occurs. An increase in the organ is fixed similarly to its growth during pregnancy - , and the growth of the tumor often becomes visible visually - the woman's belly grows as during pregnancy.
Severe bleeding during menstruation, as well as between periods, can lead to post-hemorrhagic anemia, accompanied by fainting, fatigue, lack of vitamins and soreness.
The danger of formation on the pedicle is the torsion of the pedicle, as a result of which the tumor may die. In this case, necrotic processes occur in the organ, which can cause peritonitis or general sepsis.
Very often, fibroids can cause infertility (by blocking the passage of sperm), miscarriage or premature birth.
If the doctor shows the removal of myomatous nodes, you should not refuse the operation. Otherwise, the growth of the tumor can lead to a danger to the life and health of the woman.
At what size are removed
The size of fibroids is one of the main indications for surgery to remove it. So at what size is myoma removed?
An operation is performed when the size of the uterine fibroids exceeds 3 cm. A tumor of this size most often already manifests itself in the form of the main symptoms (heavy bleeding, pain syndromes). The more actively the tumor grows, the faster it needs to be operated on.
However, there are cases that require surgical intervention for small fibroids. For example, a small neoplasm on a pedicle during torsion causes severe pain; in this case, fibroids cannot be removed without removal.
In extremely rare cases, when biopsy scrapings show cancer cells even in a small tumor, immediate surgery is required.
Also read, in what cases, together with fibroids.

Symptoms
Symptoms of fibroids usually occur when the tumor has outgrown the latent period of growth, its size is more than 2 cm.
In this case, the following symptoms of the disease may appear:
- violation of the menstrual cycle;
- bleeding not associated with menstruation;
- excessively heavy menstruation;
- frequent, sometimes painful urination;
- constipation;
- a feeling of fullness or pressure in the lower abdomen;
- pain in the abdomen, sometimes in the lower back.
Tumor growth over time becomes visible to the naked eye - in the absence of an increase in total body weight, the abdomen increases in volume.
NOTE!
If any of the symptoms of myomatous nodes appear, you should consult a gynecologist.
It is impossible to diagnose fibroids on the basis of indicators, since many other gynecological diseases can have similar symptoms. Diagnostic measures will help not only to correctly identify the disease, but also exclude deadly pathologies, such as cancer.
Diagnostic methods
What should be done to identify uterine mimoma?
The methods of conservative therapy include:
- reception;
- therapeutic baths;
- taking vitamin complexes;
In addition, indicators for conservative treatment are:
- pregnancy planning;
- localization of nodes in the muscle layer of the organ;
- there is no submucosal tumor.
In case of intolerance to anesthesia or the impossibility of performing an operation for health reasons conservative treatment is used involuntarily.